Airway Management Training: Essential Skills for Medical Professionals
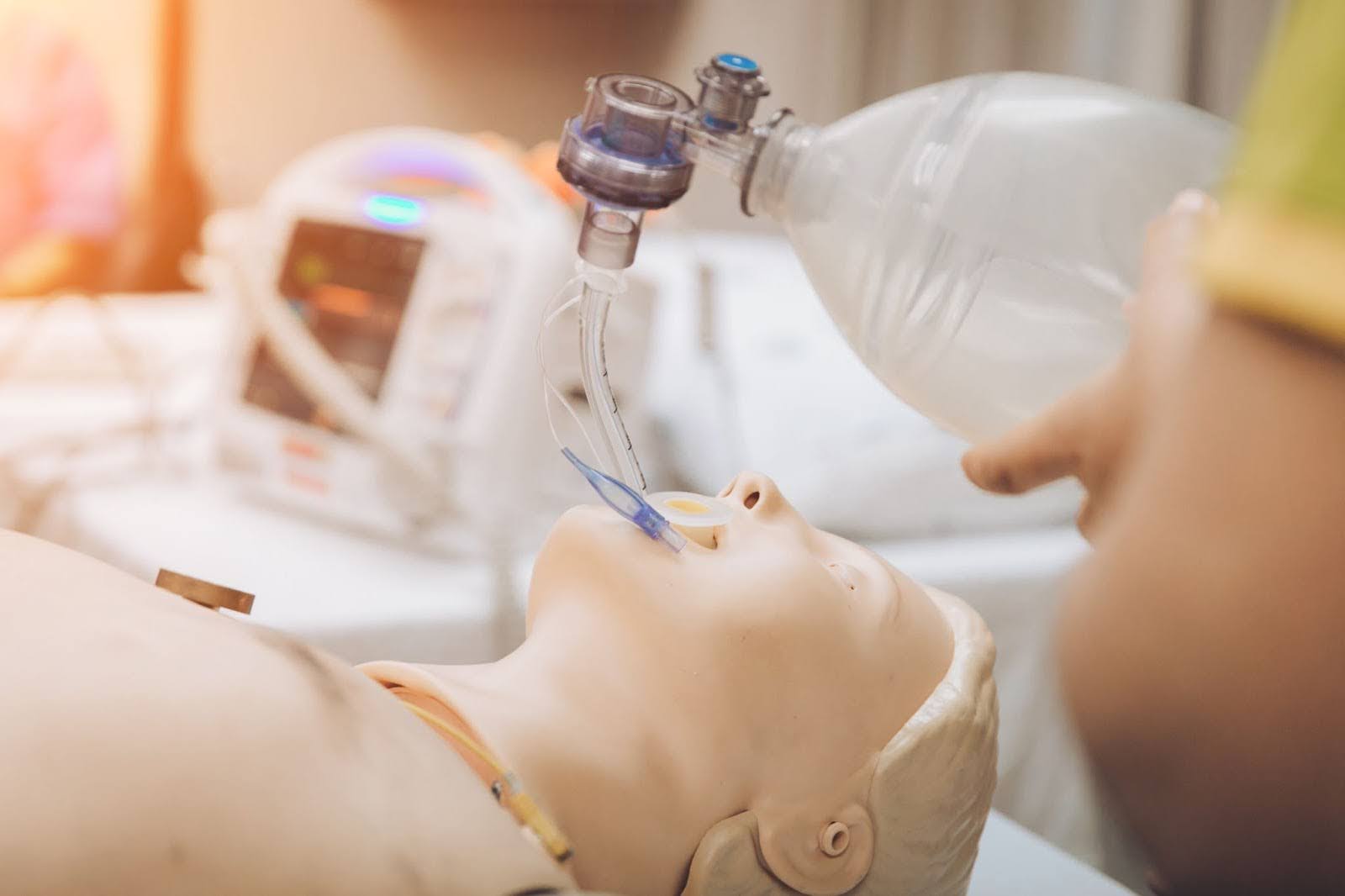
Effective airway management is a fundamental skill for medical professionals, crucial for ensuring patient safety and successful outcomes in emergency and surgical settings. Airway management training equips healthcare providers with the knowledge and techniques necessary to maintain and secure a patient’s airway, preventing complications and improving patient care.
What is Airway Management?
Airway management refers to the process of ensuring that a patient’s airway is open and clear, allowing for adequate ventilation and oxygenation. This is a critical aspect of patient care, particularly in emergency situations and during surgical procedures.
Research by NCBI shows that the inability to ventilate lungs is associated with severe complications, including mortality. Proper airway management can significantly reduce the risk of such complications, making it an essential skill for healthcare providers.
Overview of Airway Management Training
Airway management training encompasses a range of techniques and procedures designed to maintain an open airway. These techniques include manual methods, the use of airway adjuncts, and advanced procedures such as intubation. Training programs typically cover the following key areas:
- Basic Airway Management: Techniques such as head-tilt/chin-lift, jaw-thrust maneuver, and the use of bag-valve masks.
- Use of Airway Adjuncts: Devices like oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airways that help keep the airway open.
- Advanced Airway Techniques: Procedures such as endotracheal intubation, laryngeal mask airway insertion, and surgical airway management.
- Emergency Airway Management: Protocols and rapid response techniques for managing airway emergencies in various clinical scenarios.
Maintaining an open airway is crucial in both emergency and surgical settings, as it ensures that the patient receives adequate oxygenation and ventilation. This can be the difference between life and death, making airway management training a vital component of medical education and professional development.
Key Techniques in Airway Management
Effective airway management involves several key techniques that are crucial for ensuring patient safety and successful outcomes. These techniques include endotracheal intubation, the use of supraglottic airway devices, and bag-valve-mask ventilation. Hands-on training with cadaveric specimens is vital for mastering these skills, providing medical professionals with realistic practice scenarios.
This is where whole body donation plays a crucial role, offering invaluable learning experiences. For more information on how body donations support medical training, visit our body donation to science page
Endotracheal Intubation
Endotracheal intubation is a procedure where a tube is inserted into the trachea to maintain an open airway. This technique is essential for patients who are unable to breathe on their own or require mechanical ventilation.
- Indications: Respiratory failure, general anesthesia, and protection of the airway in cases of severe trauma or neurological impairment.
- Equipment Used: Laryngoscope, endotracheal tube, stylet, suction device, and a bag-valve-mask for pre-oxygenation.
- Step-by-Step Process:
- Preparation: Gather all necessary equipment and pre-oxygenate the patient.
- Positioning: Position the patient in the “sniffing” position to align the airway axes.
- Insertion: Use the laryngoscope to visualize the vocal cords and insert the endotracheal tube through the vocal cords into the trachea.
- Verification: Confirm tube placement by auscultation of breath sounds, observing chest rise, and using capnography to ensure proper ventilation.
Supraglottic Airway Devices
Supraglottic airway devices are alternative tools used to maintain an open airway, positioned above the vocal cords. These devices are particularly useful when intubation is difficult or contraindicated.
- Benefits: Easier and quicker to insert compared to traditional intubation, useful in emergency situations, and can be a temporary solution before definitive airway management.
- Types of Devices: Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA), i-gel, and King LT.
- Procedure:
- Preparation: Select the appropriate size of the device and lubricate it.
- Insertion: Open the patient’s mouth and insert the device along the hard palate until resistance is felt.
- Inflation: Inflate the cuff (if applicable) to seal the airway.
- Verification: Confirm placement by checking for breath sounds and chest rise, and secure the device.
Why Choose MERI for Airway Management Training?
MERI state-of-the-art facilities are available for use by organizations looking to conduct specialized medical training. Companies and training providers have the unique opportunity to utilize our cadaveric specimens to deliver hands-on educational experiences.
Explore Our Comprehensive Curricula
Various training sessions are conducted by external professionals who make use of our facilities and anatomical resources. By exploring our curricula, you can learn about the wide range of medical education programs hosted at MERI, including:
- Comprehensive Airway Management Training: Programs that cover basic to advanced airway management techniques, designed to equip medical professionals with essential, life-saving skills.
- Cadaveric Training for Realistic Practice: Utilizing donated bodies, these sessions provide an unmatched opportunity for participants to gain practical experience and an in-depth understanding of human anatomy.
- Simulation and Real-Life Scenarios: Our facilities support the integration of real-life medical scenarios, helping trainees apply their skills in environments that simulate actual emergencies.
For details on the types of training hosted at MERI, explore our Airway Management Training at MERI and other training programs at MERI.
The value of hands-on practice and continuing education is greatly enhanced by the availability of cadaveric specimens, made possible through body donation to science. This allows trainees to gain invaluable experience that is critical for their professional growth.
